In the realm of modern manufacturing and prototyping, the choice between a CNC machine and a 3D printer is a crucial consideration for beginners. Both technologies offer unique advantages and are pivotal in transforming ideas into tangible products. However, understanding the fundamental differences between a CNC machine and a 3D printer is essential for anyone looking to dive into the world of fabrication.
A CNC machine operates by removing material from a solid block to create precise parts, which makes it ideal for tasks that require high accuracy and durability, particularly in metal or woodworking. On the other hand, a 3D printer builds objects layer by layer, allowing for more complex shapes and designs that would be challenging to achieve through traditional subtractive methods. The two technologies cater to different needs and preferences, which can be overwhelming for beginners trying to determine the best option for their projects.
In this guide, we will explore the core differences between these two fabrication methods, highlighting their capabilities, applications, and suitability for various types of projects. By demystifying the characteristics of a CNC machine and a 3D printer, newcomers can make informed choices that align with their creative and technical goals.
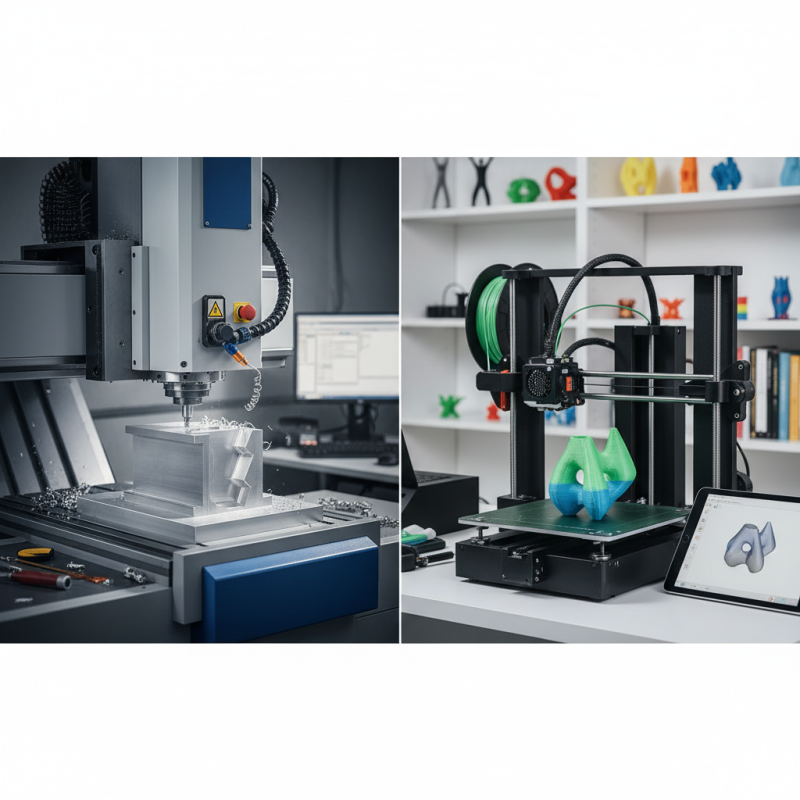

CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, represent a significant advancement in manufacturing technology. These machines operate by precisely removing material from a workpiece based on programmed instructions. The process begins with designing a part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which is then converted into a format that CNC machines can interpret. The machines follow these instructions meticulously, allowing for high precision in cutting, milling, and drilling various materials such as metal, wood, and plastic.
The versatility of CNC machines makes them widely applicable across numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, and woodworking. They can produce intricate components that are not only consistent in quality but also efficient to manufacture, reducing the likelihood of waste.
From creating complex molds to crafting customized items, CNC technology is critical in modern production workflows. By automating machinery, businesses can scale their operations while maintaining high standards of accuracy and repeatability, transforming the landscape of manufacturing and fabrication.
3D printers operate on the principle of additive manufacturing, which involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer. This process begins with a digital model designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The printer reads this model and extrudes material, typically thermoplastic filament, resin, or powder, that solidifies to form the desired shape. The layer-by-layer construction allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that are often difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
The use cases for 3D printing are vast and span several industries. In prototyping, designers can quickly produce functional models to test for fit and form, significantly accelerating the development cycle. In the medical field, 3D printing is used to create custom prosthetics and dental implants tailored to individual patients. Additionally, in manufacturing, the technology has gained traction for producing small batches of parts, allowing for rapid customization and reducing waste. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications and innovations are expanding, making it an increasingly valuable tool across various sectors.
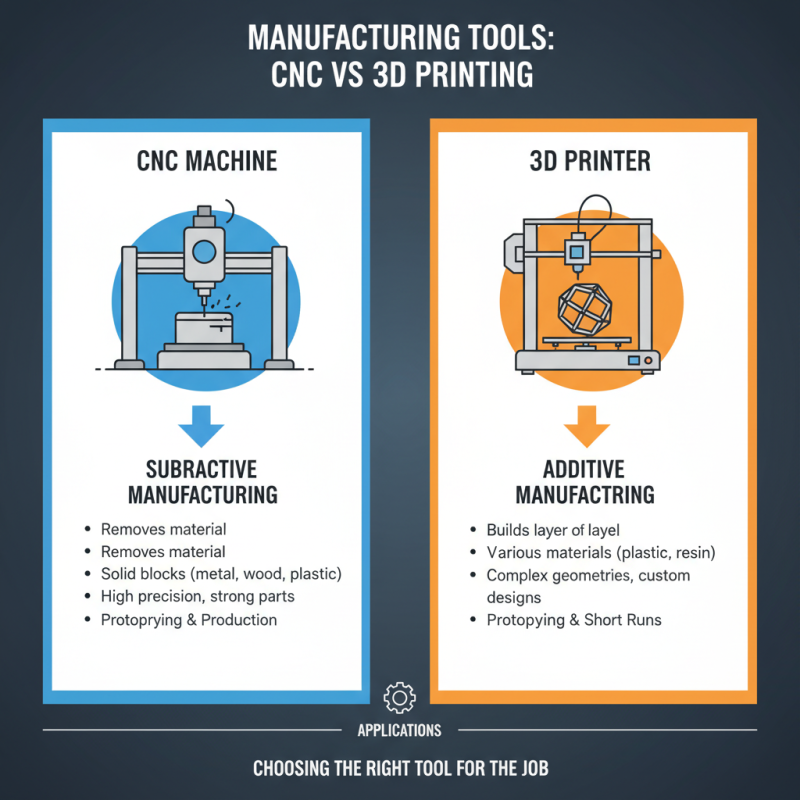
CNC machines and 3D printers are popular tools in manufacturing and prototyping, each with unique capabilities and applications. The primary difference lies in their fabrication techniques. CNC machines operate by subtractive manufacturing; they remove material from a solid block to create the desired shape. In contrast, 3D printers use additive manufacturing; they build objects layer by layer from a digital model, which allows for complex geometries that might be difficult to achieve with CNC machining.
According to a report from the Wohlers Associates 2021, the additive manufacturing industry has seen exponential growth, reaching an estimated $12.6 billion in global revenues. This growth reflects the increasing demand for rapid prototyping and customization that 3D printing offers. CNC machines, on the other hand, are favored for their precision and efficiency in mass production, particularly in metalworking and woodworking, where data indicates they dominate with over 70% market share in industrial applications.
Tips: When deciding between CNC and 3D printing, consider the materials you plan to use. CNC is ideal for metals and harder materials, while 3D printing excels with plastics and flexible materials. Additionally, understanding the complexity of your design can guide you to the most suitable option, as 3D printing is generally better for intricate designs, while CNC is favored for simpler, more robust structures.
CNC machining and 3D printing are two popular manufacturing processes, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages that cater to different needs. CNC machines utilize subtractive manufacturing, which means they cut away material from a solid block to create parts. This process allows for a high degree of precision, making CNC ideal for producing parts with tight tolerances. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global CNC machining market is expected to grow to $100 billion by 2026, demonstrating its sustained demand in industries like aerospace and automotive.
On the other hand, 3D printers employ additive manufacturing, layering material to construct objects from a digital design. This method is advantageous for creating complex geometries and customized designs with minimal waste. A study by Wohlers Associates indicates that the 3D printing industry could reach $35 billion by 2024, reflecting its emerging role in rapid prototyping and small-batch production. However, 3D printed materials may not always match the mechanical properties of traditionally machined parts, which is a consideration for certain applications.
Tips: When deciding between CNC machining and 3D printing, assess your project requirements. For high-volume production with stringent quality controls, CNC may be preferable. In contrast, for rapid prototyping and unique designs, 3D printing offers greater flexibility. Understanding the specific strengths and weaknesses of each method is crucial to making an informed decision about which technology best suits your needs.
| Aspect | CNC Machine | 3D Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Subtractive manufacturing (removes material) | Additive manufacturing (adds material layer by layer) |
| Material Variety | Metals, plastics, wood, composites | Plastics, resin, metals (limited) |
| Complexity | Suitable for complex geometries but requires skilled operator | Good for intricate designs and prototypes, easier for beginners |
| Speed | Fast for mass production | Slower for large prints, faster for small details |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower cost per unit in bulk | Lower initial investment, higher cost for large quantities |
| Tolerances | High precision and tight tolerances | Generally lower precision, varies by printer and technology |
| Post-Processing | Minimal for many materials | Often required to improve surface finish and strength |
When deciding between CNC machining and 3D printing for your project, it's essential to understand the unique capabilities each technology offers. CNC machines are excellent for producing precise parts from solid materials, making them ideal for applications that require high tolerances and durability, such as metal and woodworking. In contrast, 3D printers excel in creating complex geometries and intricate designs, particularly in plastics, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization.
Tips: Consider the material you plan to use for your project. If you need robust and rigid components, CNC machining may be the better choice. For flexible, lightweight designs or when you want to minimize waste, 3D printing could be the more efficient option.
Additionally, evaluate the scale of your project. CNC is often more suited for larger production runs, while 3D printing is advantageous for low-volume projects or one-off designs. Understanding the requirements of your project will help you choose the right technology that aligns with your goals and resources.
This chart compares CNC Machines and 3D Printers based on cost, speed, and material variety, providing insights to help beginners choose the right technology for their projects.







© Copyrights Levil Technology Corp 2022